Commonly used in several industries, including adhesives, petroleum, cleansing/lubricating products, confectionary and more, internal gear pumps are one of the key pieces of industrial equipment in the production line. What is an internal gear pump and how does it work? What roles does it play in industry? The following article explores the intricacies of internal gear pumps.
What is an Internal Gear Pump?
An internal gear pump is a type of positive displacement pump that uses two rotating, interlocking gears, specially designed to handle and transfer high viscous fluids. The rotor gear (exterior driven, outer gear) has teeth projecting on the inside of the pump and the smaller idler gear rests off center, inside the rotor gear. The idler gear is positioned off center to be able to interlock with the rotor gear, so that the gear teeth engage at one point in the pumping cycle. A pinion and bushing attached to the pump casing holds the idler gear in position. A fixed, crescent shaped partition is used as a spacer, filling the void left by the idler gear being positioned off center. The partition is used to seal liquid between the inlet and outlet ports.
Photo Credit to: Blackmer Pumps
How Does an Internal Gear Pump Work?
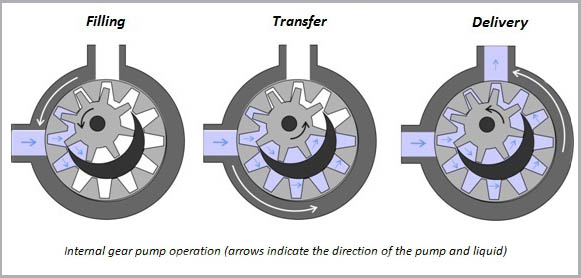
The cycle begins with liquid entering the suction port between the rotor gear and the idler gear. As the gears rotate to the suction phase of the cycle, the teeth of the gears come out of the pump’s mesh and an atmospheric vacuum (suction) is created at the inlet side, drawing liquid into the cavities. The liquid in the cavities is sealed by the gear teeth and continues to rotate against the pump casing and partition as the cycle continues. The sealed fluid is moved from the inlet to the discharge around the casing. The seal created by the gear teeth at the discharge side of the pump reduces the fluid volume and the fluid is discharged under pressure.
Photo Credit to: Michael Smith Engineers LTD
What are the Benefits of an Internal Gear Pump?
One of the primary benefits of an internal gear pump is their ability to pump high viscosity liquids such as petroleum or chocolate and thinner liquids like fuel or oil. They can also be engineered (using metal alloys or composite materials) to pump aggressive media, such as sulfuric acid and sodium hydroxide. Internal gear pumps have accurate flow control since output is directly proportional to gear rotational speed. This makes internal gear pumps ideal for metering and blending operations. With only minimal moving parts, Internal gear pumps are easy to maintain, simple to use and consistently reliable. Internal gear pumps are also bi-directional. The internal spur gears enable flow in either direction, making them perfect for filling or emptying containers.
What are the Disadvantages of an Internal Gear Pump?
Internal gear pumps can pump fluids of nearly any viscosity, but for thicker materials pump speed must be reduced, therefore extending process times. Inevitably the gears, casing and bearings in internal gear pumps will wear out over time and a pump replacement may need to be in order. Large solids can easily damage internal gear pumps due to small working tolerances. Abrasive media with small, suspended solids can be handled by internal gear pumps, but it will reduce the pump’s efficiency and potentially its lifespan depending on usage. Internal gear pumps fall victim to a process known as “flow slip” over time largely because of increased clearances and efficiency reduction. Flow slip is leakage of a pumped fluid from the discharge side back to the suction side. Flow slip can initially have a small effect on efficiency, but the problem can increase over time until a critical point is reached. This usually happens with materials that can harden, like adhesives.
What are Common Applications for Internal Gear Pumps?

Pictured: Liquid Soap Production Line at Chemicals Factory
Internal gear pumps excel at pumping clean, high viscosity media such as chocolate, asphalt and adhesives for a wide temperature range (500+ degrees for certain pump models). They are also, commonly used for thin liquids like juices, solvents, fuel and oil. Some common applications that use internal gear pumps are:
• Resins and Polymers
• Molten Sulfur
• Adhesives
• Liquid Terminals
• Soap & Detergents
• Edible Fat and Oils
• Lube Oils
• Asphalt Roofing
• Asphalt Emulsion
• Asphalt Hot Mix
To review, an internal gear pump is a type of positive displacement pump that is excellent at pumping high viscous media at wide temperature ranges (500+ degrees in some cases), but at relatively low pressures. It works using an off-center idler gear, nesting inside a rotor (exterior driven, outer gear), that creates a liquid seal with the pump casing and creates suction at the pump inlet. The sealed liquid (between gear teeth) is then transferred around the pump casing until it is expelled at the discharge outlet. The pump is low maintenance, bi-directional and has accurate flow control. An internal gear pump, however, is not a great choice for pumping media with large solids or an aggressive media with floating solids.
